In the world of men’s health, the prostate plays a quintessential role, yet it often goes unnoticed until it starts creating problems. Among the numerous issues associated with it, a swollen prostate definitely tops the list. This condition, which may put a damper on the everyday activities of numerous men, especially those in their 50s and beyond, is a matter that deserves more spotlight. Hence, this comprehensive guide is tailor-made to bring you up to speed about everything concerning a swollen prostate, from understanding its roots to its common symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures.
So, buckle up, for we are about to embark on a quest to unravel the truths about this common, yet often underestimated condition. Let’s navigate together on this manly journey to a better and healthier prostate
Table of Contents
Understanding the Prostate

What is the Prostate?
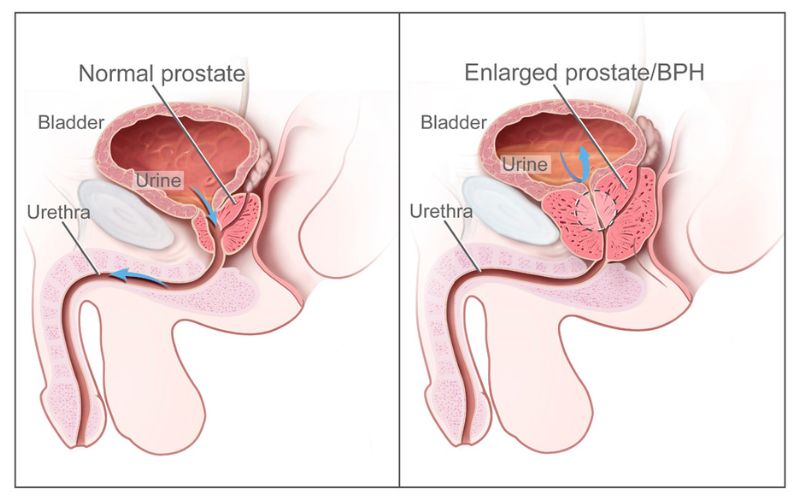
The prostate is a small but essential part of the male reproductive system. The gland is approximately the size of a walnut, weighing roughly 20 to 30 grams. It is nestled deep inside the pelvis, located between the bladder and the penis, and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine and semen exit the body.
The primary role of the prostate is to produce and secrete a fluid that nourishes and protects the sperm. This prostate fluid is a key component of semen–it makes up about 30% of the total ejaculate. The fluid is milky or white in appearance and it serves to nourish the sperm and enhance their ability to move, thereby increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
Furthermore, the prostate is also responsible for secreting prostate-specific antigen (PSA), an enzyme that aids in sperm motility. A higher-than-normal level of PSA can indicate possible prostate issues, such as inflammation or malignancy, thereby making PSA an important marker for diagnostic purposes.
Additionally, during ejaculation, the prostate and the seminal vesicles contract to propel the semen into the urethra and onward out of the penis.
In essence, despite its small stature, the prostate is vital for the fertility and overall reproductive health of men, as well as urinary control. It also plays a role in sexual pleasure, adding a layer of complexity and significance to this compact but mighty gland. Hence, maintaining a healthy prostate is integral to a man’s quality of life.
Why does the Prostate Swell?
The swelling of the prostate, medically known as prostatitis or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), can occur due to a variety of reasons.
One of the most common causes of prostate swelling is age. As men grow older, it’s natural for the prostate to increase in size. It’s a normal part of aging, much like how hair turns grey. In fact, BPH is so common that it’s said by the age of 60, about half of men will have some degree of BPH. By the age of 85, that number is up to 90%.
Another reason why the prostate might swell is due to hormonal changes. Male hormones, specifically testosterone and its byproduct dihydrotestosterone (DHT) play a crucial role in the growth of prostate cells. Any changes or imbalances in these hormones can cause the prostate to swell.
Infections can also result in a swollen prostate. This condition, known as bacterial prostatitis, occurs when bacteria in the urinary tract cause an infection in the prostate. The infected prostate then swells up, causing pain and discomfort, along with urination issues.
Another less common cause includes the development of abscesses in the prostate, where a cavity fills up with pus causing the prostate to swell up. These abscesses are usually a complication of bacterial prostatitis.
Finally, unhealthy lifestyle habits, including poor diets, obesity, and lack of physical activity, can also contribute to prostate swelling, as these factors increase the risk of inflammation and hormonal imbalance in the body.
Therefore, the swelling of the prostate can result from a variety of factors, some modifiable and others not so much. This underlines the importance of regular health checks and maintaining a healthy lifestyle as a preventative measure.
Common Symptoms of a Swollen Prostate
Difficulty in Urination
A standout symptom of a swollen prostate is the difficulty in urination, a condition medically referred to as dysuria. The urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body, passes right through the center of the prostate. Therefore, when the prostate swells, it constricts the urethra, causing an obstruction or narrowing of the passage.
This act is just like stepping on a garden hose, the water flow is hindered; in this case, that’s your urine flow! The urinary symptoms resulting from this can be particularly troubling and may include:
- Trouble starting a urine stream: Despite having the urge to go, you may find it challenging to start urinating, often needing to strain or push before the urine starts to flow.
- Weak or interrupted urine flow: Once the flow starts, it might be weak or get interrupted frequently, leading you to spend a long time in the bathroom.
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying: Even after urination, you might have a lingering sensation that your bladder is not entirely empty. This feeling can be uncomfortable and may trigger frequent trips to the bathroom.
- Straining to urinate: The need to push or strain to initiate and maintain urine flow is another sign of trouble. Straining over time can lead to other complications like urinary tract infections or bladder stones.
- Dribbling at the end of urination: This may involve leakage or dribbling of urine shortly after finishing urination, an annoying problem that can also lead to hygiene issues or skin irritation.
Difficulty in urination can significantly impact a man’s quality of life. Hence, any changes in urination habits should be discussed with a healthcare provider to diagnose a swollen prostate or any other underlying issues. Remember, it’s always better to reveal than to conceal when it comes to your health.
Frequent Urge to Urinate
An increased frequency of urinating is a classic sign of a swollen prostate. It can occur during the day, at night (known as nocturia), or both, and can severely disrupt daily activities and sleep patterns.
As the prostate gland enlarges and puts pressure on the urethra, it can partially block the flow of urine. This blockage can trick the bladder into thinking it needs to get rid of urine when it doesn’t need to, leading to a persistent feeling that one needs to go to the bathroom.
A sizeable prostate may also stop the bladder from completely emptying during urination, leaving some urine behind. As the bladder fills again with fresh urine from the kidneys, it triggers the need to urinate sooner than usual due to the limited capacity.
That being the case, you may find yourself running to the restroom frequently. Whether you are in the middle of a meeting, a good night’s sleep, or a long road trip, it may feel like your bladder just can’t seem to hold on as it used to.
This frequent urge to urinate can also occur in tandem with other symptoms, such as difficulty starting urination, a weak urine stream, or a sudden, overwhelming urge to urinate with the inability to control it, leading to embarrassing instances of urinary incontinence.
While many men experience these changes as they grow older, it’s crucial to discuss them with a healthcare professional. The sudden urge to go, frequent visits to the bathroom, or waking up constantly throughout the night are more than just a nuisance – they are signs that should not be ignored.
Pain or Discomfort
Experiencing pain or discomfort is another symptom often associated with a swollen prostate. This symptom can manifest in various ways and can sometimes be confusing as the discomfort can be felt in places beyond just the prostate region.
The Nature of the Pain: The pain and discomfort related to a swollen prostate can be characterized as dull, throbbing, or intense depending upon the severity of the inflammation.
Location of the Pain: While the discomfort could be felt directly in the area of the prostate, it could also radiate to other parts of the lower body. Some of the common areas affected can include the lower back, pelvic region, hips, and thighs.
Pain During Urination: The discomfort could be particularly noticeable while urinating. The act of urination may cause a burning or stinging sensation, making each trip to the restroom an unpleasant experience.
Pain or Discomfort During Sexual Intercourse: One of the lesser-known symptoms of a swollen prostate is discomfort during ejaculation. Men may experience pain or discomfort during or after ejaculation. There might also be noticeable changes in sexual performance such as erectile dysfunction or decreased sexual desire, which could affect a person’s quality of life.
Rectal Discomfort: Considering the close proximity of the prostate to the rectum, it’s not uncommon to feel pressure or discomfort in the rectal area when the prostate is inflamed.
It’s crucial to remember that while a certain level of discomfort might be common, especially as one ages, significant pain or a sudden increase in discomfort, should never be ignored. It’s always best to consult a healthcare professional to get the appropriate treatment and to rule out any serious underlying conditions. Pain is the body’s way of signaling that something is off-balance and it’s not something one should have to live with.
Diagnosing a Swollen Prostate
Physical Examination
The diagnosis journey for a swollen prostate typically begins with a physical examination. The objective of this initial step is to allow the healthcare provider to assess your condition, provide a proper diagnosis, and design an apt treatment strategy. Here’s how it generally unfolds.
The cornerstone of the physical examination to diagnose a swollen prostate is the Digital Rectal Exam (DRE). Though perhaps uncomfortable, it is a crucial step and remarkably quick.
During the DRE, the doctor will insert a gloved and lubricated finger into the rectum as the prostate is directly accessible through the thin wall of the rectum. This allows them to physically feel the prostate gland and assess its size, shape, and texture.
The doctor will be checking for any abnormalities. For instance, a healthy prostate has a consistent, smooth texture and size similar to a walnut. Contrastingly, a swollen prostate may feel larger and tougher. They’ll also look for any nodules or areas of hardness that might indicate the presence of a tumor.
By performing the DRE, the doctor will be able to tell if the prostate is enlarged or if it has areas with abnormal textures, both possible indicators of a swollen prostate or related conditions such as prostate cancer.
Even though the thought of the procedure can make one squeamish, it’s critical to remember that the DRE is administered by trained professionals and only takes a few minutes. The valuable information that it provides in return outweighs the brief discomfort. Therefore, if you are experiencing symptoms suggestive of a swollen prostate, let your doctor know promptly. After all, it’s your health!
Blood Tests
During the diagnostic process for a swollen prostate, doctors often rely on blood tests as a key step. The main blood test used is the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test. This test measures the amount of PSA, a type of protein produced by the prostate gland, present in the patient’s blood.
Typically, a high level of PSA in the blood can be a potential sign of prostate disorders such as prostatitis, an enlarged prostate, or at worst, prostate cancer. However, other non-prostate-related factors like age, certain medications, and even rigorous physical activities could also cause PSA levels to rise temporarily, hence it’s not a definitive indicator.
Though not the only factor in diagnosing a swollen prostate, the PSA test is a very useful tool in the process. It guides the physician on whether to proceed with further diagnostic investigations like imaging tests or even a biopsy. To be noted, elevated PSA levels necessitate a more in-depth examination as it could be indicative of more serious problems.
The procedure is as simple as a normal blood test and involves drawing a small blood sample from a vein in the arm. The collected sample is then sent to a laboratory where the amount of PSA is measured. It’s important to discuss the results of the PSA test and their implications with your doctor to understand the best course of action.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests form a critical part of the diagnosing process for a swollen prostate, providing healthcare professionals with a detailed look at the prostate and surrounding areas. These insights can help in determining the severity of the condition and guide the appropriate course of treatment.
There are a few types of imaging tests commonly used in this process:
- Ultrasound: During a prostate ultrasound, a small probe about the size of a finger is inserted into the rectum. This procedure, also known as a Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS), uses sound waves to create an image of the prostate gland. It is often used along with a biopsy to assess the prostate’s condition accurately.
- MRI Scan: For more detailed imaging, doctors may resort to an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan. This technology gives a more comprehensive picture of the prostate gland and can give finer details about any abnormalities. An MRI can be particularly helpful if the PSA levels are high, suggesting potential serious complications like prostate cancer.
- CT Scan: Although less common for diagnosing a swollen prostate, CT (Computed Tomography) scans may be utilized when the doctor suspects the problem might have spread beyond the prostate. This imaging test is more focused on examining the entire pelvic area and can be helpful in detecting if there’s any spread to nearby tissues.
While the thought of these tests might sound intimidating, they are generally safe and vital in providing a complete understanding of the prostate’s health. The test chosen will depend on an individual’s specific symptoms and the doctor’s judgment based on the initial physical examination and blood test results.
Swollen Prostate Treatment Options

Medications
A swollen prostate can be a significant cause of discomfort, and in many cases, medications are the first line of defense to alleviate this condition. Your healthcare provider is likely to prescribe medication based on the severity of your symptoms and general health. Let’s consider these various medicinal routes in more detail:
- Alpha Blockers: These medications work by relaxing the muscles in the bladder and prostate, making it easier to pass urine. Examples include terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, and alfuzosin. They usually start acting quickly, and symptoms typically improve within days to weeks.
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: These medications are generally reserved for larger prostates. They work by shrinking the prostate, thereby relieving urinary symptoms. It may take up to six months to a year to see improvements though. Finasteride and dutasteride fall within this category.
- Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors: You might be familiar with these as treatments for erectile dysfunction, but drugs like sildenafil and tadalafil can also treat prostate problems. They serve by relaxing smooth muscle and enhancing blood flow in the prostate region, alleviating urinary symptoms.
- Beta-3 adrenergic agonists: These medications, like mirabegron, can help relax the muscles of the bladder, making it easier to urinate.
- Combination Therapy: In some cases, doctors might suggest a combination of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and alpha-blockers to manage symptoms more effectively.
Remember, all medications might bring along potential side effects, which can range from simple issues like headaches, nausea, and mild dizziness to more serious ones like lowered sex drive or even erectile dysfunction. It’s essential to discuss these with your doctor and inform them of any other medications you are currently on to avoid negative interactions.
A pill may not be the cure-all, but it can be the crucial first step toward managing your swollen prostate.
Surgical Procedures
When the swollen prostate condition escalates to a point where medications aren’t effective, a surgical procedure may be the best recourse. There are several types of surgeries, so let’s look at a few of the commonly recommended ones by healthcare providers.
One of the most standard procedures is the Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). During TURP, surgeons remove portions of the prostate tissue that are causing issues with the urine flow. The entire procedure is done through the urethra, which cancels the need for any external cut on your body. Ingenious, isn’t it?
Another approach is the Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE). In this minimally invasive treatment, tiny particles are injected into the arteries feeding the prostate, which helps in shrinking the prostate gland. The appeal of this procedure is that it requires no anesthesia and has a lesser recovery period.
Lastly, Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL) is an option where tiny implants are used to lift and hold the enlarged prostate tissue out of the way, minimizing the obstruction to the urethra. This procedure is a good choice for patients looking for a less invasive treatment option.
It’s crucial to remember that every procedure has its own pros and cons. Therefore, discuss these options with your doctor before deciding what’s best for you because the end game here is a healthy and comfortable life.
Alternative Treatments
When conventional treatments don’t quite hit the mark, or if you prefer a more holistic approach, alternative treatments can offer a beacon of hope in the management of a swollen prostate.
The first approach is the use of herbal remedies. For centuries, many cultures have been harnessing the healing power of plants to manage health issues, including a swollen prostate. One of the most popular and researched herbal solutions is saw palmetto. This plant extract is believed to help shrink the prostate and alleviate the pesky urinary symptoms. Pygeum, an extract from an African plum tree, has shown similar promise, as has Rye grass pollen and Stinging nettle. But, be warned! While these remedies might sound “natural and harmless,” they could lead to adverse effects, therefore always talk to your healthcare provider if you plan to start any herbal regimen.
The second approach is based on lifestyle changes. And no, it’s not just about switching up your jogging route or trying out a new salad cafe. Lifestyle changes in relation to a swollen prostate are targeted adjustments that can significantly aid your health. These may include engaging in regular lower-body exercises, maintaining a well-balanced diet, limiting fluid intake before bedtime to reduce nighttime urination, and refraining from alcohol and caffeine as they stimulate urine production.
Finally, a complementary technique called Acupuncture can help manage the symptoms of a swollen prostate. This traditional Chinese method uses fine needles to stimulate certain points on the body, lifting the energy blockages, and improving the overall function of the urinary system.
Remember, when it comes to alternative treatments, selecting the most effective one requires a deep understanding of your condition, a dash of patience, and collaboration with your health provider. With the right decisions, you could be on the road to improved prostate health, one step at a time.
Herbal Remedies
Prostate issues don’t always require a pill from a bottle. Many men have found relief from symptoms of prostate enlargement by using herbal remedies. These remedies often are chosen as an alternative or supplement to conventional medical treatments.
For instance, Saw Palmetto, an extract derived from the fruit of the Serenoa repens tree, has gained popularity over the years for its potential beneficial effects on the prostate. It has been suggested to help with urinary symptoms that come with BPH such as frequent urination and difficulty completely emptying the bladder.
Beta-Sitosterol, a substance found in many plants, is another herbal remedy that’s been demonstrated to improve urinary flow and reduce the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination. This could potentially alleviate some of the symptoms of prostate enlargement.
Pygeum, derived from the African plum tree, is another alternative remedy that has long been used for urinary health. It’s said to reduce inflammation, improve urinary flow, and decrease nighttime urination.
Remember, even though these herbal remedies are natural, it doesn’t mean they’re risk-free. Discuss with your doctor before starting any of these, as they may cause side effects and interact with other treatments or medications you’re taking.
Lifestyle Changes

Lifestyle modifications can significantly influence the state of an enlarged prostate and alleviate your symptoms. Here are some changes you could incorporate for a healthier prostate:
Diet: Try swapping out red meats, processed foods, dairy, and sugar for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Foods such as salmon, tomatoes, berries, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli have been found to be beneficial for prostate health.
Exercise: Regular physical activity is excellent not only for overall health but specifically for preventing prostate issues. In particular, pelvic strengthening exercises, like Kegels, can help in improving urinary control.
Healthy Fluid Intake: While staying hydrated is necessary, excessive fluid intake can lead to frequent urination, especially at night. Avoid drinking fluids two hours before bedtime to minimize sleep disruptions.
Limit caffeine and alcohol: These substances can aggravate the urinary system and increase the frequency of your bathroom visits. Try to reduce intake of these, especially in the evening.
Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk of severe prostate issues and can make the existing ones worse. Hence ditching this habit can greatly improve prostate health.
Stress Management: High-stress levels or anxiety can exaggerate urinary issues. Considering stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and relaxation exercises can be of substantial assistance.
Making changes in your lifestyle can be a low-risk way to treat prostate-related symptoms. However, consult your doctor before implementing any major changes to your daily routine.
Swollen Prostate Prevention and Management
Diet and Nutrition
In the fight against a swollen prostate, your kitchen could as well become your primary battlefield. Incorporating certain foods in your diet can greatly benefit your prostate health. Diet might not cure an already swollen prostate, but it can certainly play an instrumental role in preventing and managing the condition.
When it comes to optimum prostate health, fruits and veggies should be your best friends. They are jam-packed with vitamins and antioxidants that can combat inflammation in your body, including your prostate. Among fruits, tomatoes deserve a special mention. They are bursting with lycopene, a potent antioxidant that’s been shown to be beneficial for prostate health.
The goodness of whole grains cannot be stressed enough either. They are brimming with fiber which can not only aid in digestion but might also help in keeping your prostate in check. Swapping white bread and pasta with their whole-grain counterparts could be a clever move for your prostate.
Last but certainly not least, fatty fish like salmon and mackerel could be fantastic for your prostate too. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids which are known for their strong anti-inflammatory properties.
So the next time you visit the grocery store, steer your cart towards these prostate-friendly foods. Because it’s not just food, it’s nourishment for your prostate!
Regular Check-ups

Regular check-ups and screenings form the cornerstone of any broader strategy aimed at maintaining a healthy prostate and overall wellness. Without these check-ups, conditions such as a swollen prostate might fly under the radar until they cause significant discomfort or complications.
Typically, doctors recommend that men begin routine prostate screenings at the age of 50. However, if you have risk factors such as a family history of prostate issues or are of African descent, your doctor might recommend you start earlier.
Prostate screenings generally involve two types of tests – a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test. In a DRE, your doctor inserts a gloved finger into your rectum to physically check for any abnormalities in the prostate. Yes, it might sound a bit off-putting, but it’s a quick and usually painless way to detect problems early.
The PSA test, on the other hand, involves testing your blood for elevated levels of a protein produced by your prostate. High levels of PSA can indicate an enlarged or inflamed prostate or even prostate cancer.
Remember, early detection drastically improves the odds of successfully managing and treating a swollen prostate. It might feel like a chore at times, but regular check-ups are essential for keeping your prostate healthy. So make sure you keep those doctor appointments – your prostate will thank you!
Conclusion
In conclusion, a swollen prostate, while being a common issue for men, especially as they age, can be effectively managed and treated with the right care. From understanding the role of the prostate and recognizing the symptoms to seeking appropriate diagnosis and treatment, every step is crucial. Whether it’s through medications, surgical procedures, or lifestyle modifications, every treatment serves its purpose. The key lies in regular check-ups and early detection, ensuring a healthy lifestyle is maintained. Never ignore the signs your body gives you, it’s the main way it communicates. Remember, your health is in your hands!
FAQs
1. What are the first signs of a swollen prostate? The early signs often revolve around changes to your urination frequency and flow. There might be an increased urge to urinate and also difficulty while starting or stopping the pee.
2. Can a swollen prostate go away on its own? Although mild inflammation might subside with time and lifestyle interventions, it’s crucial to seek medical advice to diagnose and accurately treat the condition.
3. How long does it take for a swollen prostate to heal? The healing duration varies depending on the severity, treatment type being administered may range from a few weeks to several months.
4. What foods are bad for your prostate? Processed and fried foods, red meats, dairy products, and foods with high levels of sugar are known to negatively influence prostate health.
5. Can exercise help my swollen prostate? Yes! Exercises (especially those targeting the pelvic muscles) can aid in managing the symptoms but should be accompanied by medical treatments for full efficacy.